What is Avalanche?
Introduction
Avalanche is an open-source platform for launching decentralized applications and enterprise blockchain deployments in one interoperable, highly scalable ecosystem. Avalanche is the first decentralized smart contracts platform built for the scale of global finance, with near-instant transaction finality. Ethereum developers can quickly build on Avalanche as Solidity works out-of-the-box.
A key difference between Avalanche and other decentralized networks is the consensus protocol. Over time, people have come to a false understanding that blockchains have to be slow and not scalable. The Avalanche protocol employs a novel approach to consensus to achieve its strong safety guarantees, quick finality, and high-throughput without compromising decentralization.
AVAX
AVAX is the native token of Avalanche. It’s a hard-capped, scarce asset that is used to pay for fees, secure the platform through staking, and provide a basic unit of account between the multiple subnets created on Avalanche. 1 nAVAX is equal to 0.000000001 AVAX.
Avalanche Consensus Protocol

Protocols in the Avalanche family operate through repeated sub-sampled voting. When a validator is determining whether a transaction should be accepted or rejected, it asks a small, random subset of validators whether they think the transaction should be accepted or rejected. If the queried validator thinks the transaction is invalid, has already rejected the transaction, or prefers a conflicting transaction, it replies that it thinks the transaction should be rejected. Otherwise, it replies that it thinks the transaction should be accepted.
If a sufficiently large portion (alpha α) of the validators sampled reply that they think the transaction should be accepted, the validator prefers to accept the transaction. That is, when it is queried about the transaction in the future, it will reply that it thinks the transaction should be accepted. Similarly, the validator will prefer to reject the transaction if a sufficiently large portion of the validators replies that they think the transaction should be rejected.
The validator repeats this sampling process until alpha of the validators queried reply the same way (accept or reject) for beta β consecutive rounds.
In the common case when a transaction has no conflicts, finalization happens very quickly. When conflicts exist, honest validators quickly cluster around conflicting transactions, entering a positive feedback loop until all correct validators prefer that transaction. This leads to the acceptance of non-conflicting transactions and the rejection of conflicting transactions.
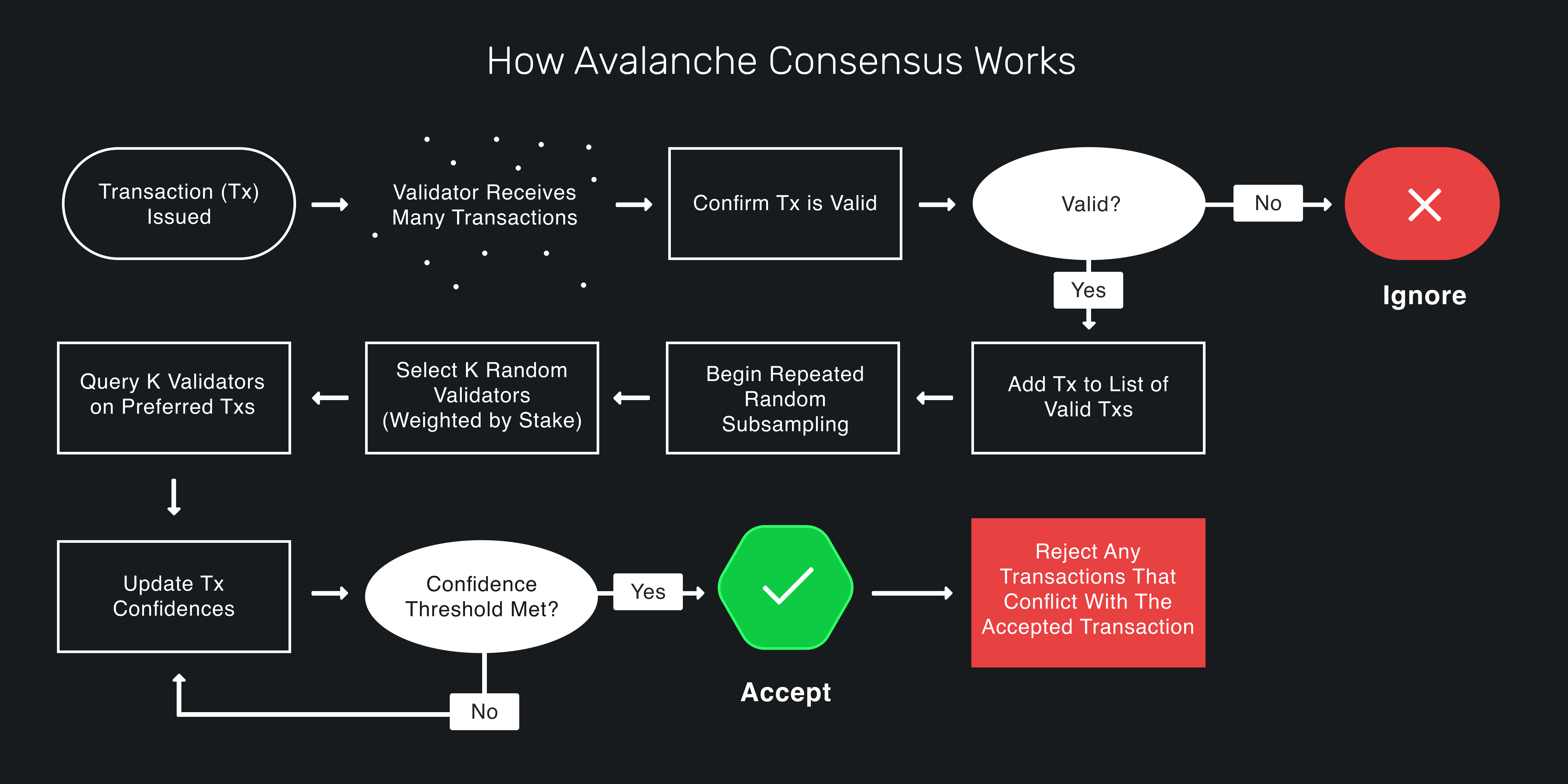
It is guaranteed (with high probability based on system parameters) that if any honest validator accepts or rejects a transaction, all honest validators will accept or reject that transaction.
Learn more technical components of the Avalanche consensus protocol by reading the whitepaper.
Snowman Consensus Protocol
Snowman is a chain-optimized consensus protocol–high-throughput, totally-ordered, and great for smart contracts. Snowman is powered by the Avalanche consensus protocol. Both P-Chain and C-Chain implement the Snowman consensus protocol.
Key Features
Speed
Uses a novel consensus protocol, developed by a team of Cornell computer scientists, and is able to permanently confirm transactions in under 1 second.
Scalability
Capable of 4,500 transactions per second–an order of magnitude greater than existing blockchains.
Security
Ensures stronger security guarantees well-above the 51% standard of other networks.
Flexibility
Easily create custom blockchains and decentralized apps that contain almost any arbitrary logic.
Sustainability
Uses energy-efficient proof-of-stake consensus algorithm rather than proof-of-work.
Smart Contract Support
Supports the creation of Solidity smart contracts and your favorite Ethereum tools like Remix, Metamask, Truffle, and more.
Private and Public Blockchains
Create your own public or private blockchains.
Designed for Finance
Native support for easily creating and trading digital smart assets with complex, custom rulesets.